Nitrile Rubber Products for Sealing and Insulation
 When is nitrile rubber the right choice for sealing and insulation? This common elastomer is known by many names, including Buna-N, NBR, and acrylonitrile butadiene. There are plenty of trade names for nitrile, too. No matter what you call it, nitrile rubber offers good resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals. Temperature and environmental conditions are limiting factors, however, and may require the selection of a more expensive material such as Viton™.
When is nitrile rubber the right choice for sealing and insulation? This common elastomer is known by many names, including Buna-N, NBR, and acrylonitrile butadiene. There are plenty of trade names for nitrile, too. No matter what you call it, nitrile rubber offers good resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals. Temperature and environmental conditions are limiting factors, however, and may require the selection of a more expensive material such as Viton™.
In this article from Elasto Proxy, you’ll learn about nitrile’s advantages and disadvantages. You’ll also examine NBR compounds, compare commercial and specialty Buna-N, and consider some typical nitrile applications. Elasto Proxy supplies specialty nitrile products to a variety of industries and can create a custom sealing solution that meets your specific requirements. Nitrile isn’t the only oil-resistant elastomer, but it’s a cost-effective choice compared to some other compounds.
Nitrile Advantages and Disadvantages
 Nitrile rubber provides good-to-excellent resistance to many oils and solvents. Examples include:
Nitrile rubber provides good-to-excellent resistance to many oils and solvents. Examples include:
- animal and vegetable oils
- crude petroleum oil
- kerosene and gasoline
- liquified petroleum (LP) gases
- motor oils
- mineral oil based hydraulic fluids
- silicone greases and oils
For engineers and buyers, it’s important to understand that nitrile’s resistance to petroleum oils is limited by temperature. According to most chemical resistance charts, nitrile resists petroleum oil at temperatures up to 250° F (121° C). If your application requires both oil resistance and higher temperature resistance, a fluorocarbon such as Viton™ may be required instead. Nitrile is also unsuitable for highly polar solvents such as acetone, which is used in some food processing and medical applications.
Nitrile’s advantages include good physical properties such as resistance to compression set, tearing, and abrasion. Typically, NBR or Buna-N comes in durometers (Shore A) ranging from 20 to 95 for applications that require a softer or harder rubber. Nitrile resists water, but provides poor resistance to weather, ozone, and aging. Acrylonitrile butadiene is also unsuitable for some applications because Buna-N won’t withstand temperatures that are colder than -40° F (-40° C).
Nitrile Compounds and Specialty Grades
Through compounding, material suppliers have developed different types of nitrile with enhanced material properties. For example, hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR) can withstand slightly higher temperatures than NBR and provides improved resistance to polar fluids. Carboxylated nitrile butadiene rubber (XNBR) has a higher compression set than Buna-N and offers improved tear and abrasion resistance. Nitrile can also be blended with polymers such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
For engineers and buyers, choosing the right type of nitrile may involve comparing commercial rubber to specialty grades. Commercial grades generally cost less and are available in higher minimum order quantities (MOQs). Specialty grades generally cost more and have larger MOQs, but they’re custom compounds with improved properties. ASTM D2000 provides a standard way to describe elastomers and uses the designations BF, BG, BK, and CH with both standard and specialty nitrile. (more…)
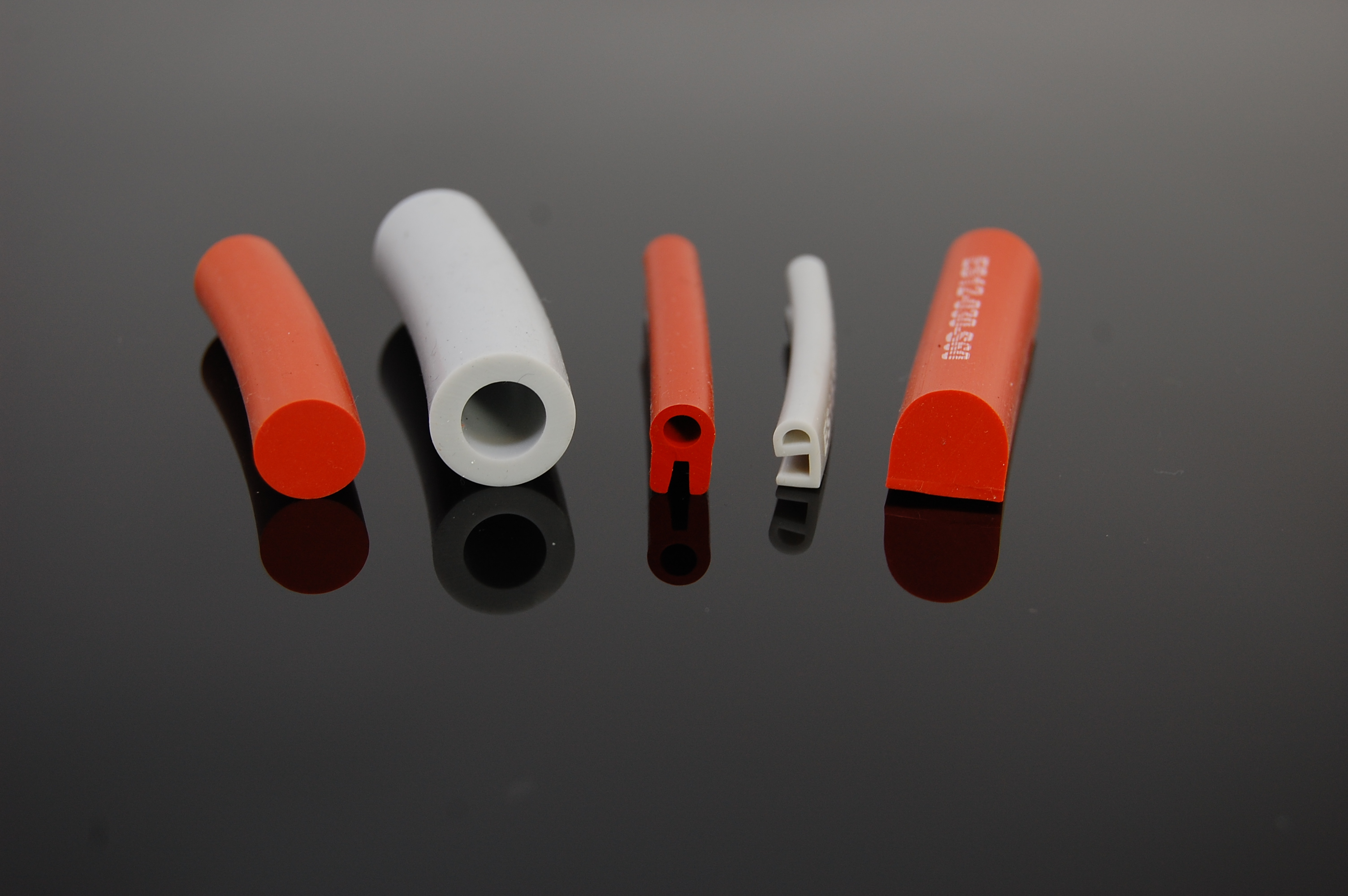


 Commercial grade rubber provides sealing and insulation for a wide variety of applications. Compounds such as commercial grade EPDM, silicone, and neoprene also cost less than specialty rubber materials that meet standards, approvals, or regulatory requirements from organizations such as ASTM International, Underwriters Laboratories (UL), and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Commercial grade rubber provides sealing and insulation for a wide variety of applications. Compounds such as commercial grade EPDM, silicone, and neoprene also cost less than specialty rubber materials that meet standards, approvals, or regulatory requirements from organizations such as ASTM International, Underwriters Laboratories (UL), and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
 The Elasto Proxy Blog is starting the New Year with a quick look back at how we helped readers solve their sealing and insulation challenges in 2017. Whether you’re new to the Blog or a veteran reader of our 275 posts, we hope you’ll enjoy this review and will let us know what you’d like to read about in 2018.
The Elasto Proxy Blog is starting the New Year with a quick look back at how we helped readers solve their sealing and insulation challenges in 2017. Whether you’re new to the Blog or a veteran reader of our 275 posts, we hope you’ll enjoy this review and will let us know what you’d like to read about in 2018. Learn about bulb trim seal measurements from Elasto Proxy.
Learn about bulb trim seal measurements from Elasto Proxy. 
 How is silicone rubber used for sealing and insulation? Silicones have valuable properties, but engineers need rubber that meets specific requirements. If you’re wondering whether silicone seals, gaskets, or insulation are the right choice for your application, consider some of the uses for this versatile polymer. The examples you’ll read about aren’t the only uses for silicone, but they’re representative.
How is silicone rubber used for sealing and insulation? Silicones have valuable properties, but engineers need rubber that meets specific requirements. If you’re wondering whether silicone seals, gaskets, or insulation are the right choice for your application, consider some of the uses for this versatile polymer. The examples you’ll read about aren’t the only uses for silicone, but they’re representative.