Electric Vehicles - Products & Solutions
Page Contents
Design Considerations

EVs are powered by the electricity from a rechargeable battery. ICE vehicles ignite and combust fuel within an internal combustion engine (ICE) instead. You probably knew this already, but did you know that ICE vehicles and EVs also share many components in common?
For example, EVs and ICE both have gears and electric motors, use transmission fluid and coolants, and have braking and safety systems. In addition, designers of ICE and electric vehicles are adding an increasing amount of electronic content that can cause electromagnetic interference (EMI).
The Electrification of Everything

For engineers in the heavy equipment and transportation industries, the electrification of everything can present challenges both old and new.
For example, designers of diesel-powered equipment have long wanted to reduce the amount of engine noise that reaches the cabin. EVs eliminate engine noise because they use a battery, but they still need acoustic insulation because road noise is now more pronounced. Regardless of a vehicle’s powerplant, problems such as buzz, squeak and rattle (BSR) from a faulty door or window seal also remain unwelcome.
The main difference between ICE vehicles and EVs is about what generates the power for movement, but there’s so much more to consider. The table below provides a comparison.
Table 1: ICE Vehicles vs. EVs
Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicle | Electric Vehicle (EV) |
High specific energy fuel | Low specify energy of battery |
Emits greenhouse gases | No tailpipe emissions |
Travels >600km / fill | Travels <250km / charge |
Short refilling time (<5 min.) | Long charging time (0.5 to 8 hrs.) |
Fuel tank takes relatively little space | Battery takes large space |
Fuel weight is low | Batteries are very heavy |
Higher maintenance cost | Lower maintenance cost |
Braking energy is not recovered | Can recover braking energy |
Running cost: high | Running cost: low |
Energy efficiency: 30% | Motor efficiency: 80% |
Needs complex gear system | Needs only one gear |
Noisy operation | Quiet operation |
Ample refilling infrastructure | Lacks charging infrastructure |
Need to pick up speed to deliver maximum torque | Produces maximum torque |
Uses only hydrocarbons | Uses electricity from many sources |
Let’s take a closer look at what EV designers who are used to working with ICE vehicles need to consider.
Electric Motors and EMI Shielding

EVs and ICE vehicles both use electric motors, devices that supply motive power to either the vehicle itself or to another system. EV motors are larger than ICE motors, but both of these motors have two parts: a rotor that turns, and a stator that does not.
In ICE vehicles, the stator touches the rotor through brushes and a commutator. A chemical reaction in the battery generates direct current (DC), which produces a magnetic field and spins the rotor. This rotation is transferred to the engine until the first ignition. Once the engine is started, rotation is transferred into motion.
In EVs, the stator does not touch the rotor. A chemical reaction in the battery generates DC current, but this DC is converted into alternating current (AC). In turn, the AC creates a magnetic field that causes the rotor to spin and transfers this rotation into movement.
In both ICE and electric vehicles, there are electromagnetic fields between the rotor and stator. ICE vehicles generate these fields for just a short period of time, but EVs generate fields that are stronger and last longer. Consequently, EV designers need EMI gaskets to seal and insulate housings and enclosures for sensitive electronics.
Chemical Energy and Energy Density
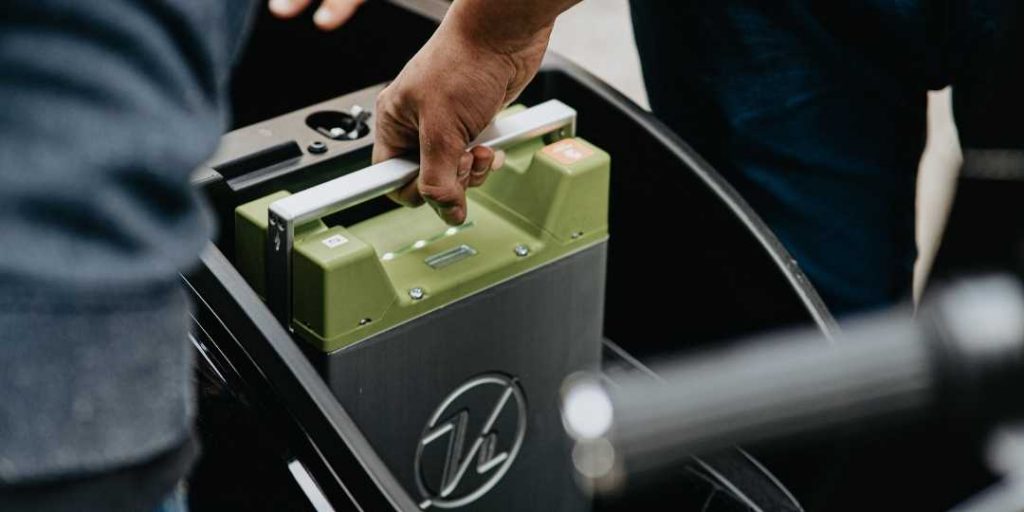

ICE vehicles and EVs both convert chemical energy into motion. For the internal combustion engine, this chemical energy comes from a fuel like gasoline or diesel. With EVs, the chemical energy comes from a rechargeable battery.
Because gasoline and diesel are relatively lightweight but produce a high amount of power, they have high energy density. By contrast, EV batteries are heavy (500 kg) and have a low energy output. Consequently, EV power sources have a relatively low energy density – a potential problem with heavy trucks, trains, or buses that need significant energy to move a load.
Electric vehicles use a lower-density energy source, but EVs also use lighter weight components. For example, in many diesel-powered heavy trucks, door seals are made of EPDM rubber, an economical and weather resistant elastomers. Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPVs) elastomers weigh significantly less than thermoset EPDMs and are finding applications in electric vehicles. High-performance TPVs with high heat resistant and excellent oil resistance are also used in under-the-hood ICE applications.
Efficiency, Torque and Weight

There are also differences between ICE vehicles and EVs in terms of efficiency. For example, ICE vehicles convert the reciprocating, or up-and-down, movement of pistons into rotary motion. This conversion causes a major loss of efficiency and produces significant friction and vibration.
Electric vehicles don’t need to convert reciprocating motion into rotary motion because the EV’s electric motor is already spinning. This leads to a 50% gain in efficiency (30% for ICE vs. 80% for EV) with only minimal friction and vibration. There are also differences in torque, a measure of the force that causes an object to rotate on an axis.
Vehicles with internal combustion engines have multiple gears, including for low and high speeds, to meet revolutions per minute (RPM) requirements for torque. The speed of rotation is controlled by the throttle, and the RPM range for optimal torque is between 2000 and 8000.
By contrast, electric vehicles have only one gear and support a wider range of RPM. The speed of rotation is controlled by the frequency of the AC current, and the range for optimal torque is between 0 and 20,000 RPM. With their heavy batteries, however, the weight of a typical EV (610 kg) exceeds that of an ICE vehicle (240 to 480 kg).
Environmental Sealing and Thermal Insulation

Both ICE and electric vehicles need industrial rubber that can provide strong environmental resistance. Rain, snow, dirt, rust, road salt, and other contaminants from outside the vehicle need to be sealed-out and automotive fluids need to be sealed-in and kept clean.
Compared to ICE vehicles, EVs store less liquid. There’s no fuel tank, of course, but EVs also need less transmission fluid. During the seal design process, however, it’s important to consider if an EV will be exposed to different types of chemicals.
Vehicle designers also need to consider that that EV battery packs must be kept cool during recharging. If one of the batteries in a pack overheats, the potential thermal runaway may ignite the other batteries in the pack. These battery packs are also sensitive to puncture and, once pierced, can leak electrolytes. Punctured batteries may also overheat when charging.
Products and Materials
Electric vehicles use materials ranging from metals and ceramics to the lithium, nickel and cobalt in EV batteries. For sealing and insulation, however, rubber and plastic are used. Whether they’re extruded, molded, rubber-to-metal bonded, or custom fabricated, EV manufacturers need specific types of seals, gaskets, and insulation. Here are the top ten types of EV products that Elasto Proxy provides.
EV Door Seals
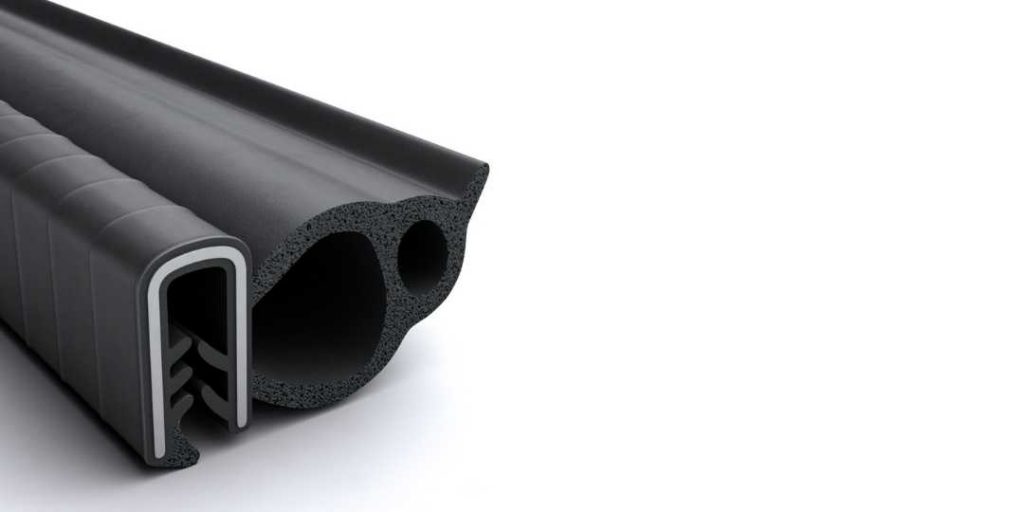

Elasto Proxy makes EV door seals from extruded lengths of TPV or EPDM rubber. TPV is more expensive, but it’s lighter-weight, recyclable, and supports color matching. EPDM is a traditional automotive material, but it can be coated to avoid squeaking and discoloration. We can supply you with coils or cut lengths, but you’ll get even greater value from bonded gaskets that are taped for peel-and-stick installation.
EV Window Seals
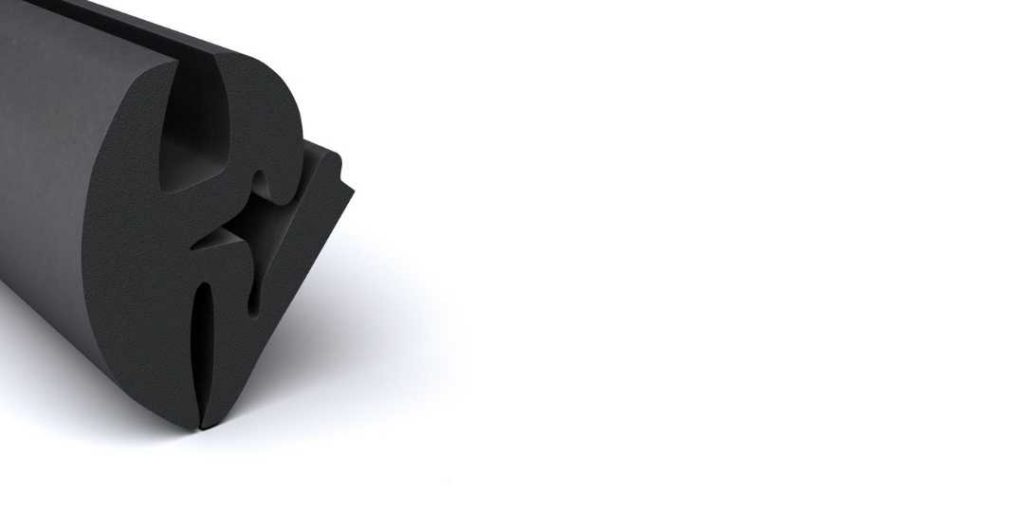

EV window seals from Elasto Proxy are made from extruded rubber that’s been flocked or coated with textile fibers to promote sealing and reduce rubbing, a cause of buzz, squeak, and rattle (BSR). Whether you need traditional glass run channels or custom gaskets for vent or valence (quarter-glass) windows, we’re ready to share installation advice and draw upon our gasketing experience.
EV Anti-Vibration Mounts
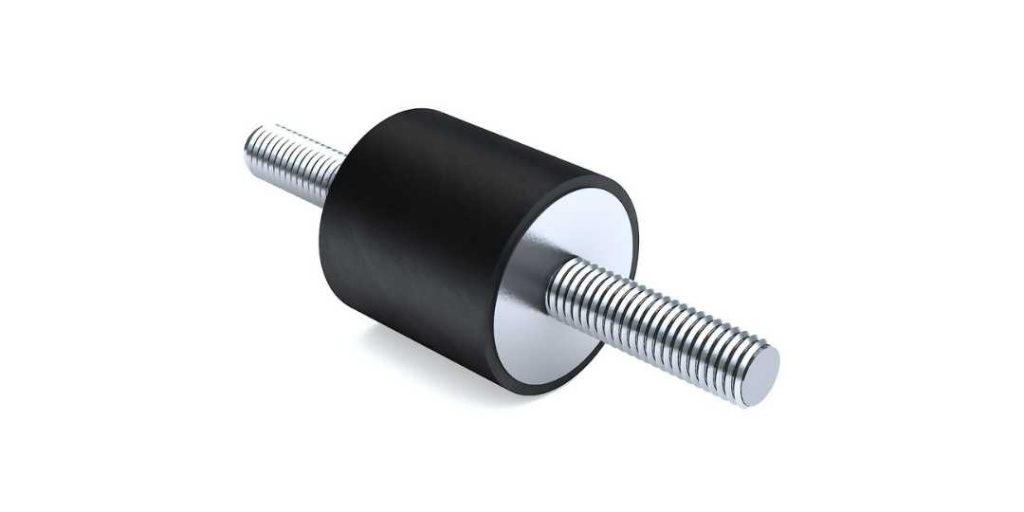

The EV anti-vibration mounts that we supply also help to reduce NVH and BSR. These rubber-to-metal bonded products include power train mounts that come in styles such as cone mounts, H-mounts, and bushes. Products also include EV suspension mounts, EV closure stops, and travel limiters. Let us help you with component selection and kit your anti-vibration mounts along with other EV products for each build.
EV Thermal Pads
EV thermal pads are made from thermally conductive silicones that help move heat away from sensitive components such as onboard electronics. Elasto Proxy fabricates thermal pads from sheets that come in a range of durometers and thicknesses. We can also supply you with molded EV products such as O-rings and grommets that are made from silicones with good thermal conductivity.
EV EMI Shielding Gaskets
As a complete provider of EV-specific solutions, Elasto Proxy offers protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI). We fabricate EV EMI shielding gaskets from silicones that contain metal or metal-coated particles. We can also supply you with molded gaskets or bonded O-rings made from these same materials. For ready-to-install EMI gaskets, ask us to apply a pressure-sensitive adhesive (PSA) tape.
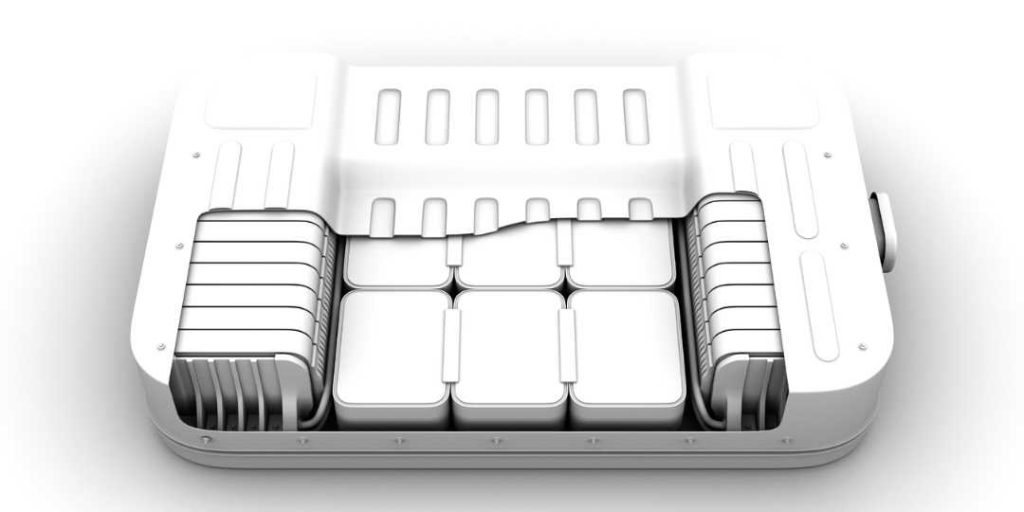
EV Battery Compartment Gaskets
Elasto Proxy’s EV battery compartment gaskets combine environmental sealing with thermal insulation. They can also deliver EMI shielding and flame resistance. These enclosure seals are installed between the top and bottom parts of the battery compartment and may have holes for metal fasteners. Choose EV battery gaskets made from silicone or polyurethane foams or consider solid silicones with UL 94 approvals.
EV Battery Pack Seals
EV battery pack seals provide sealing and insulation within the battery compartment itself. They are installed between battery packs and are often made of closed-cell silicone, a material that resists the contaminants while providing compressibility and high-temperature resistance. EV battery pack seals that are made from silicones also resist a wide range of temperatures and can provide flame resistance.
EV Hoses and Hose Connectors
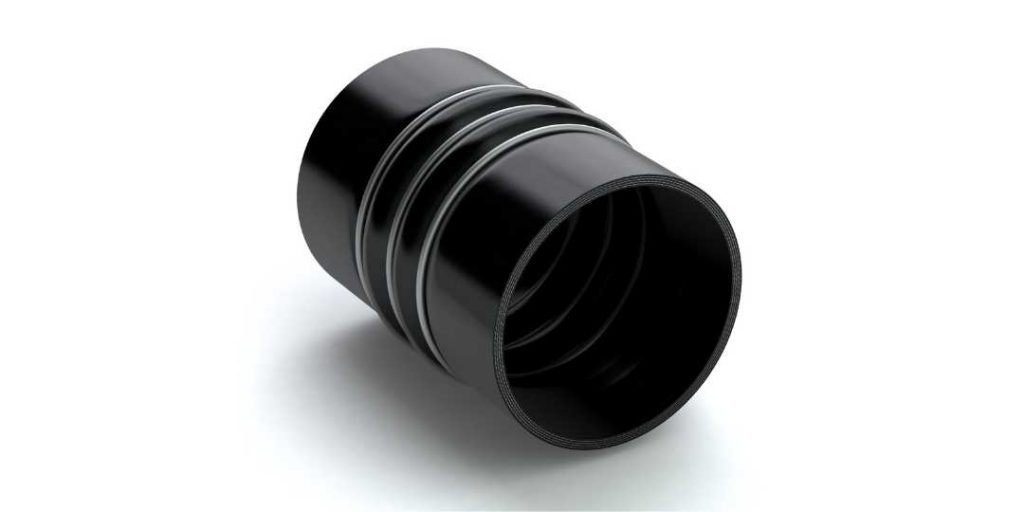

Generally, EV hoses are longer and narrower than the hoses used in ICE vehicles. In part, that’s because EVs need complex hose assemblies that wrap around the battery and the battery compartment for thermal management. Like ICE vehicles, however, EVs also use silicone hoses and connectors for air conditioning systems. Elasto Proxy is your source for them all, including EPDM hose connectors.
EV Rubber and Plastic Molded Parts

Among the many products we can provide to EV manufacturers, Elasto Proxy is also your one-shop stop for molded rubber and plastic parts. Along with connectors and anti-vibration mounts, examples include grommets, bumpers, and hose clamps. By leveraging our supply chain strength, you can simplify sourcing and add value to your operations.
Why the EV Industry is Choosing Elasto Proxy

The EV industry is moving even faster than the Aspark Owl, an electric vehicle that can accelerate from 0 to 60 mph (96.5 km/h) in just 1.69 seconds. The race to develop the world’s fastest electric car is a riveting one, but everything in the EV industry just keeps moving faster. Whether you’re an established brand or up-and-coming company, you need an edge to win.
Elasto Proxy serves the EV industry and is helping electric vehicle manufacturers to stay ahead of their competition. Whether you’re designing a car, truck, bus, train, or airplane, rubber and plastic products probably aren’t top-of-mind. What you’ll find, however, is that thinking about sealing and insulation sooner rather than later can help you get products to market faster. We can help.
It’s time to put Elasto Proxy on your team. Here are five things to expect when you work with us
• Engineering assistance
• Material selection and sourcing
• Prototyping
• Manufacturing
• Added value services
Let’s take a closer look at what you need to know.
#1 Engineering assistance that’s like having an extra member (or two) of your team

Many of the EV engineers that we speak with know how to design a rubber gasket. Yet, some add metal tolerances to part drawings, an issue that can require revisions that result in delays. When you work with Elasto Proxy, you’ll have ready access to the expertise you need. You might say that working with us is like having an extension of your engineering department. You’ll save design time, but you can also save the expense of hiring another engineer. Multiple members of our team may even participate in calls with you.
#2 Material selection and sourcing that strikes the right balance – in lower MOQs.

There isn’t just one type of “black rubber”, and you might need to make tough choices between gasket materials such as EPDM and TPV. Elasto Proxy understands the language of rubber and can help you to translate your requirements into the right solutions. Although we work with a large network of extruders, we can provide you with lower minimum order quantities (MOQs) than you’ll receive if you work with these companies directly. Plus, we offer a wide range of EV products.
#3 Prototyping that eliminates paying for or waiting for tooling.
Many of the rubber and plastic products that Elasto Proxy makes are fabricated with water jet cutting, a tool-less process that uses a highly pressurized stream of water with or without an abrasive. Instead of cutting parts by hand or waiting for tooling to arrive, you can get the prototypes you need right away – and without paying for dies, knives, CNC tools, or blades. You can validate your designs quickly, iterate them efficiently, and test similar products for differences in part dimensions such as radii.
#4 Manufacturing that takes you from product development right to production.

Water jet cutting is also a fast and cost-efficient method for low-to-medium volume production. Because there’s no tooling to wait for, you can transition from product development quickly and without delays. Elasto Proxy’s manufacturing capabilities include a choice of gasket bonding methods so that you can get mitered or molded corners. If you need thermal or acoustic insulation instead, we can laminate sheet materials in-house and then cut them precisely using our water jet equipment.
#5 Added-value services that the EV industry needs to compete and win.

Finally, Elasto Proxy offers added-value services that you won’t find just anywhere else. For example, we can manage stock level for you and store both your raw materials and your finished goods. We also provide taped gaskets and have an in-house testing laboratory. In addition, we provide kitting and custom packaging so that you can get all of the rubber and plastic parts you need for an electric vehicle, and in the proper order of installation. All your installers need to do is open the box and get to work.
Related EV Blog Topics
Lightweighting for Electric Buses
- Steve Melito
- 4 March 2024
- Electric Vehicles / Engineering
- 0 Comments
Rubber and Plastic Truck Parts for OEMs and MROs
- Steve Melito
- 7 January 2024
- Electric Vehicles / Heavy Equipment / Industry
Electric Mining Vehicles: The Role of Rubber Products
- Steve Melito
- 13 March 2023
- Electric Vehicles
- 0 Comments
Molded Rubber Parts for Electric Vehicles
- Steve Melito
- 27 February 2023
- Electric Vehicles
- 0 Comments
Sustainability and Electric Vehicle Sealing and Insulation
- Steve Melito
- 20 February 2023
- Electric Vehicles / News
- 0 Comments
Electric Vehicle Lightweighting and Rubber Products
- Steve Melito
- 13 February 2023
- Electric Vehicles
- 0 Comments
Related Products
Parts for Electric Vehicle Manufacturers

Elasto Proxy supplies manufacturers of electric vehicles with rubber seals, custom gaskets, thermal and acoustic insulation, and EMI shielding.
Within the transportation industry, here are some of the electric vehicle companies that we serve.
- Electric vehicle charging
- Hybrid electric vehicles
- Electric vehicle companies
- Electric off road vehicle
- Electric vehicle battery
- Electric vehicle motor
- Future of electric vehicles
We can also provide parts for electric trucks and have worked with manufacturers of some of the best EVs on the market today.




More for Manufacturers of Electric Vehicles
Installing a large number of electronics into a small interior space can cause these systems to interfere with each other. Malfunctions or failures caused by cross-talk aren’t the only risks, however. Strong electromagnetic fields (EMFs) can affect human health. That’s why the batteries in EVs are enclosed in more than just a metal box. A shielding gasket atop the box contains EMFs and prevents electromagnetic interference (EMI) from the battery from disrupting other electronics.
EMI gaskets are used with the inverters and converters that manage the power and recharging circuits in electric cars and hybrid electric vehicles. Shielding gaskets are also needed at EV charging stations, where multiple chargers can generate strong EMFs as well as EMI. Paying for an EV charge could pose a problem, however. Electronic cash registers have drawers for dollar bills, and point of sales (POS) systems use electronics for credit card processing. Both need EMI gasketing.
Whether you need particle-filled silicones for EMI shielding or sponge or solid silicone gaskets for sealing and insulation, Elasto Proxy can provide you with the solutions that you need.
Sponge Rubber Gaskets vs. Solid Rubber Gaskets
Download the Ultimate Guide for Electric Vehicles. It is FREE!